The first and only oral BTK inhibitor for CSU1
RHAPSIDO® (remibrutinib) is a highly selective BTK inhibitor2,*
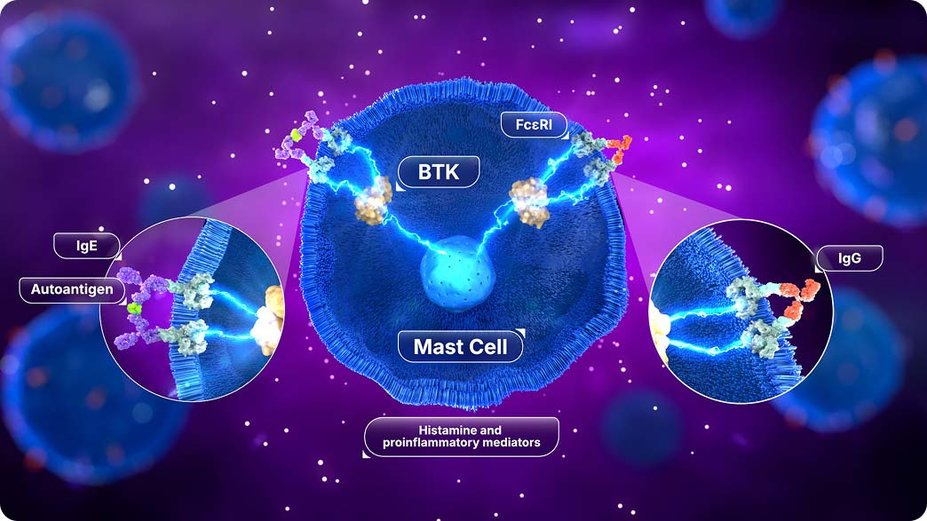
RHAPSIDO helps to inhibit the release of histamine and other proinflammatory mediators.1
Watch the targeted MOA in action
*RHAPSIDO also inhibits the BTK-related kinases TEC and BMX. In a preclinical study, RHAPSIDO demonstrated high affinity and selectivity for BTK, with a subnanomolar binding constant (Kd) of 0.63 nM, and a selectivity of 175-fold against TEC (Kd of 110 nM) and 857-fold against BMX (Kd of 540 nM). RHAPSIDO did not show binding to ITK, EGFR, ERBB2, ERBB4, or JAK3 at concentrations of up to 10 µM. The clinical significance of this data has not been demonstrated.1,2
BTK plays a key role in CSU3
CSU may be mediated by IgE and IgG inflammatory pathways4
BTK is expressed in select immune cells, including dermal mast cells, and can be activated by IgE (autoallergic) and IgG (autoimmune) pathways via FcεRI.3
Intracellular BTK signaling leads to mast cell degranulation and the release of histamine and other proinflammatory mediators.3
The pathogenesis of CSU has not been fully elucidated; however, it is believed to be primarily a mast cell–driven disease.4,5
RHAPSIDO offers a unique approach to CSU1
By inhibiting BTK in mast cells, RHAPSIDO blocks both IgE and IgG pathways, stopping mast cell degranulation and the release of histamine and proinflammatory mediators.1