Fast relief from hives and itch at week 121
RHAPSIDO® (remibrutinib) demonstrated consistent results in both of its phase 3 trials1
In the REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 trials, RHAPSIDO significantly improved hives, itch, disease activity and angioedema vs placebo in patients with CSU who remained symptomatic on antihistamines. The co-primary end points were absolute change from baseline in HSS7 and ISS7 at week 12.1
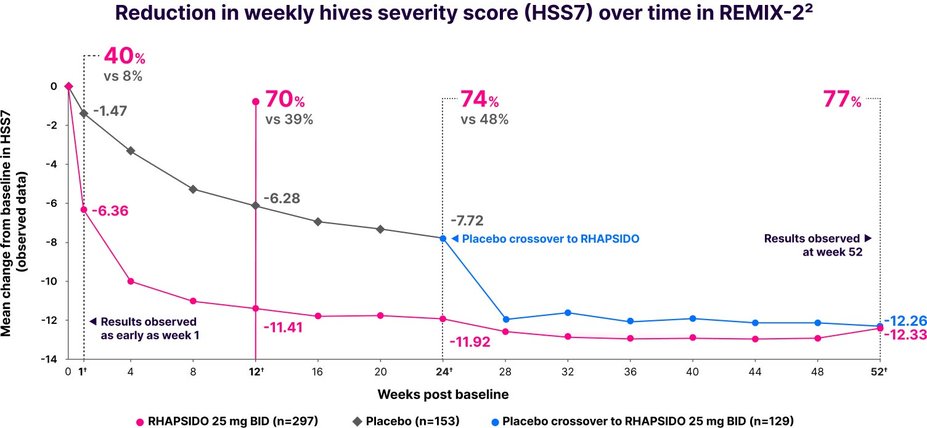
Fast relief from hives1
Significant reduction in HSS7 vs placebo at week 12: LS mean CFB -10.47 with RHAPSIDO vs -6.00 with placebo (P<.001) in REMIX-2. Similar results were observed in REMIX-1.1–3,*
Results were observed as early as week 1 in a post hoc analysis and at week 52 in an exploratory analysis.2,3,†
*Multiple imputation techniques were implemented for missing data.1
†LIMITATIONS: No conclusions or comparisons can be drawn since post hoc or prespecified exploratory analyses were performed at week 1 and weeks 12 and 24, respectively. These analyses were not adjusted for multiplicity. Data after week 24 should be interpreted with caution due to the open-label design and absence of a control group. Week 52 data is a prespecified exploratory analysis and no statistical tests were done.2,4
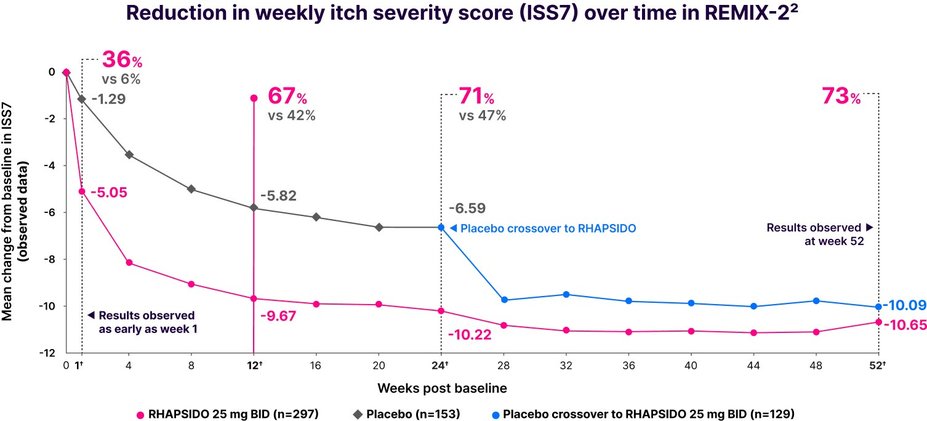
Fast relief from itch1
Significant reduction in ISS7 vs placebo at week 12: LS mean CFB -8.95 with RHAPSIDO vs -5.72 with placebo (P<.001) in REMIX-2. Similar results were seen in REMIX-1.1–3,*
Results were observed as early as week 1 in a post hoc analysis and at week 52 in an exploratory analysis.2,3,†
*Multiple imputation techniques were implemented for missing data.1
†LIMITATIONS: No conclusions or comparisons can be drawn since post hoc or prespecified exploratory analyses were performed at week 1 and weeks 12 and 24, respectively. These analyses were not adjusted for multiplicity. Data after week 24 should be interpreted with caution due to the open-label design and absence of a control group. Week 52 data is a prespecified exploratory analysis and no statistical tests were done.2,4
RHAPSIDO is proven to deliver well-controlled CSU1,4
Well-controlled CSU (UAS7 ≤6) at weeks 2 and 12 (secondary end points)1,*
*Multiple imputation techniques were implemented for missing data.1
Complete absence of hives and itch (UAS7=0)
At week 12 (secondary end point)1,*
*Multiple imputation techniques were implemented for missing data.1
Exploratory analysis at week 52 (observed data) in REMIX-22,†
†LIMITATIONS: No conclusions or comparisons can be drawn. Data after week 24 should be interpreted with caution due to the open-label design and absence of a control group. Week 52 data is a prespecified exploratory analysis and no statistical tests were done.2
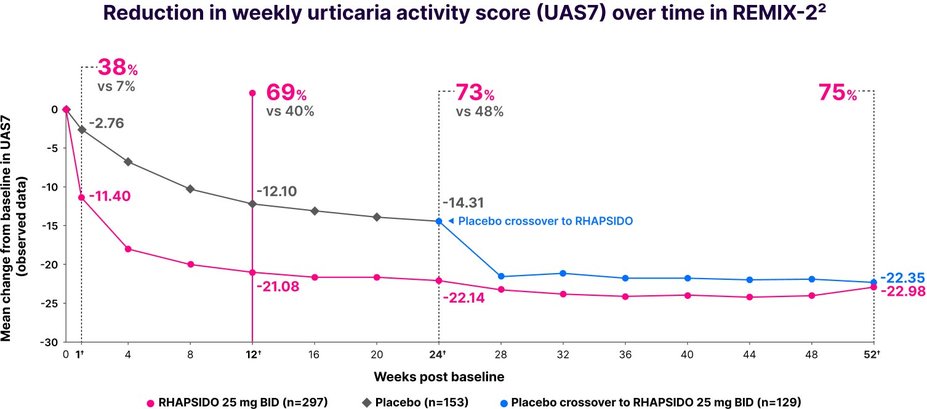
Disease activity results (UAS7)
Key secondary end point: significant reduction in UAS7 vs placebo at week 12 (LS mean CFB in REMIX-2: -19.41 with RHAPSIDO vs -11.73 with placebo; P<.001). Similar results were observed in REMIX-1.1–3,*
*Multiple imputation techniques were implemented for missing data.1
†LIMITATIONS: No conclusions or comparisons can be drawn since post-hoc or prespecified exploratory analyses were performed at week 1 and weeks 12 and 24, respectively. These analyses were not adjusted for multiplicity. Data after week 24 should be interpreted with caution due to the open-label design and absence of a control group. Week 52 data is a prespecified exploratory analysis and no statistical tests were done.2,4
Cumulative number of angioedema-free weeks (AAS7=0) with RHAPSIDO2
In REMIX-2 at baseline:
46% of patients (n=208) had prior angioedema1
Secondary end point: Cumulative, nonconsecutive, angioedema-free weeks vs placebo between baseline and week 12. Similar results were observed in REMIX-1.2,3
Cumulative number of angioedema occurrence-free weeks (AAS7=0)
Between baseline and week 12, the LS mean cumulative number of angioedema-free weeks (AAS7=0) was 8.81 with RHAPSIDO vs 6.68 with placebo.2,*